NCBI下载的10X单细胞数据只有read1和read2如何读入cellranger
10x的数据可以使用 cellranger mkfastq 产生,下面的例子是两个样本同一个lane测序拆分后分析;第二个例子是同一个样本两个lane测序,需要合并一起分析;
大家注意文件命名方式,蓝色和红色部分;
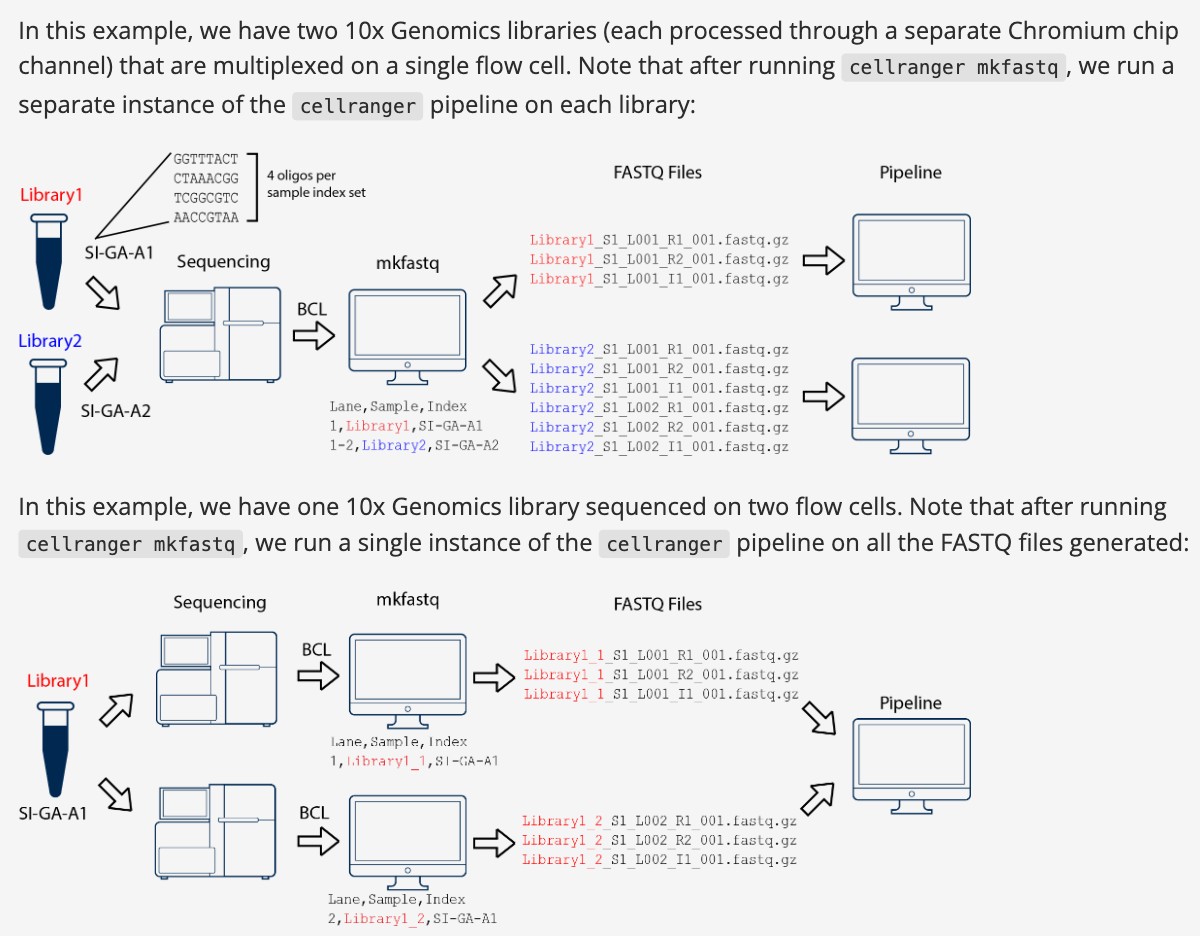
cellranger命名规则
[Sample Name]_S1_L00[Lane Number]_[Read Type]_001.fastq.gz
# 其中Read Type
# I1: Sample index read (optional)
# R1: Read 1
# R2: Read 2
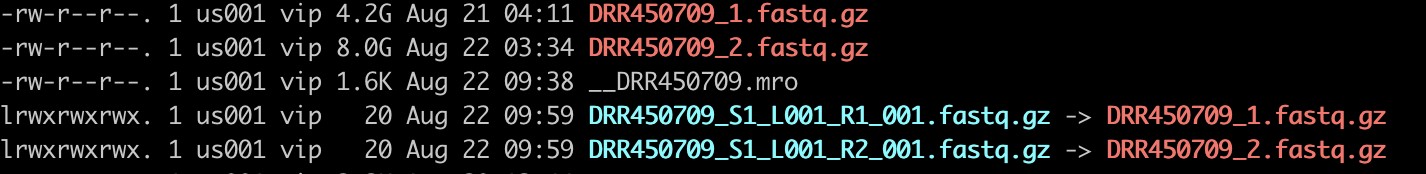
NCBI下载的数据,为双端reads,不符合cellranger mkfastq出来的命名规则,后续cellranger count 无法读入,因此我们要按上述命名规则重新命名文件:

重新命名:
ln -s DRR450709_1.fastq.gz DRR450709_S1_L001_R1_001.fastq.gz
ln -s DRR450709_2.fastq.gz DRR450709_S1_L001_R2_001.fastq.gz
cellranger命令:
cellranger count --id=DRR450709 \
--fastqs=./ \
--sample=DRR450709 \
--localcores 20 --create-bam=true \
--transcriptome=/share/ref/Homo_sapiens/refdata-gex-GRCh38-2024-A/
参考:
https://support.10xgenomics.com/single-cell-gene-expression/software/pipelines/latest/using/mkfastq
python脚本,用于链接 10X测序数据为新文件, 设置命令行参数:
#链接文件命名规则
#[Library_Name]_S1_L00[Lane_Number]_[R1/R2]_001.fastq.gz
# 其中Read Type
# R1: Read 1
# R2: Read 2
有两列表格做为输入,第1列为Run编号,第2列为 Library_Name,如果有相同的Library_Name编号 Lane_Number +1。
Run Library_Name
SRR27277573 GSM7980884
SRR27277581 GSM7980882
SRR27277619 GSM7980865
SRR27277620 GSM7980864
SRR27277621 GSM7980863
SRR27277622 GSM7980862
输入文件夹包含如下文件:
SRR27277573_1.fastq.gz SRR27277579_2.fastq.gz SRR27277586_1.fastq.gz SRR27277592_2.fastq.gz SRR27277599_1.fastq.gz SRR27277605_2.fastq.gz SRR27277612_1.fastq.gz SRR27277618_2.fastq.gz
SRR27277573_2.fastq.gz SRR27277580_1.fastq.gz SRR27277586_2.fastq.gz SRR27277593_1.fastq.gz SRR27277599_2.fastq.gz SRR27277606_1.fastq.gz SRR27277612_2.fastq.gz SRR27277619_1.fastq.gz
#!/usr/bin/env python3
import os
import argparse
from collections import defaultdict
def create_arg_parser():
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(description='Link SRA fastq to 10X library : https://www.omicsclass.com/article/2536')
parser.add_argument('-i', '--input_dir', default=os.getcwd(),
help='Input directory containing NCBI download fastq files (default: current directory)')
parser.add_argument('-o', '--output_dir', default=os.getcwd(),
help='Output directory for linked files (default: current directory)')
parser.add_argument('-t', '--table', required=True,
help='Tab-delimited table with Run and Library_Name columns')
parser.add_argument('--force', action='store_true',
help='Overwrite existing links/files in output directory')
return parser
def main():
parser = create_arg_parser()
args = parser.parse_args()
# Validate directories
if not os.path.isdir(args.input_dir):
raise FileNotFoundError(f"Input directory not found: {args.input_dir}")
os.makedirs(args.output_dir, exist_ok=True)
# Read the table
run_to_library = {}
with open(args.table, 'r') as f:
next(f) # skip header
for line in f:
parts = line.strip().split('\t')
if len(parts) >= 2:
run_to_library[parts[0]] = parts[1]
if not run_to_library:
raise ValueError("No valid entries found in the table file")
# Track lane numbers for each library
library_lane_counts = defaultdict(int)
processed_files = 0
# Process each run in the table
for run, library in run_to_library.items():
lane_number = library_lane_counts[library] + 1
library_lane_counts[library] = lane_number
# Process R1 and R2 files
for read_type in ['1', '2']:
old_file = os.path.join(args.input_dir, f"{run}_{read_type}.fastq.gz")
if not os.path.exists(old_file):
print(f"Warning: Input file not found - {old_file}")
continue
new_filename = f"{library}_S1_L00{lane_number}_R{read_type}_001.fastq.gz"
new_file = os.path.join(args.output_dir, new_filename)
# Check if target exists
if os.path.exists(new_file):
if args.force:
os.remove(new_file)
else:
print(f"Warning: Output file exists (use --force to overwrite) - {new_file}")
continue
# Create symbolic link
try:
rel_path = os.path.relpath(old_file, args.output_dir)
os.symlink(rel_path, new_file)
print(f"Created link: {new_filename} -> {rel_path}")
processed_files += 1
except OSError as e:
print(f"Error creating link {new_file}: {e}")
print(f"\nProcess completed. Successfully created {processed_files} links in {args.output_dir}")
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
- 发表于 2024-08-22 10:03
- 阅读 ( 2158 )
- 分类:转录组
你可能感兴趣的文章
- 拟南芥叶单细胞分析流程 436 浏览
- 非模式物种10X空间转录组单细胞参考基因组构建 485 浏览
- 单细胞转录组镜像代码更新4.0 1101 浏览
- 单细胞转录组数据挖掘流程记录-头颈癌(HNSCC)(GSE181919) 807 浏览
- 非负矩阵分解(cNMF) 1521 浏览
- 单细胞转录组如何将UCell CytoTRACE2 infercnv等结果添加到总的rds中 842 浏览
