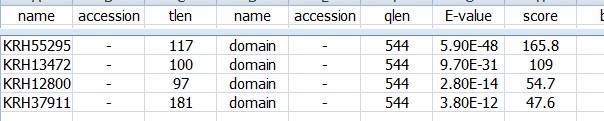
如果是用hmmsearch命令查询我们序列中的保守结构域:
target length是我们输入序列总长度;query length 输入的查询序列也就是蛋白结构域的总长度;筛选的时候不应该筛选这两个长度,没有意义;应该看后面的两个from to 看看这两条序列从哪里到哪里比对上了; 一般我们会筛选第7列的E-value值;
要知道怎么筛选先看看文件说明,以下是结构域格式输出说明,官方说明 http://eddylab.org/software/hmmer/Userguide.pdf 在我们《基因家族课程》里面也有详细说明。
The domain hits table
In protein search programs, the --domtblout option produces the domain
hits table. There is one line for each domain. There may be more
than one domain per sequence. The domain table has 22 whitespacedelimited
fields followed by a free text target sequence description,
as follows:
(1) target name: The name of the target sequence or profile.
(2) target accession: Accession of the target sequence or profile, or ’-’ if none is available.
(3) tlen: Length of the target sequence or profile, in residues. This (together with the query length) is useful for interpreting where the domain coordinates (in subsequent columns) lie in the sequence.
(4) query name: Name of the query sequence or profile.
(5) accession: Accession of the target sequence or profile, or ’-’ if none is available.
(6) qlen: Length of the query sequence or profile, in residues.
(7) E-value: E-value of the overall sequence/profile comparison (including all domains).
(8) score: Bit score of the overall sequence/profile comparison (including all domains), inclusive of a null2 bias composition correction to the score.
(9) bias: The biased composition score correction that was applied to the bit score.
(10) #: This domain’s number (1..ndom).
(11) of: The total number of domains reported in the sequence, ndom.
(12) c-Evalue: The “conditional E-value”, a permissive measure of how reliable this particular domain may be. The conditional Evalue is calculated on a smaller search space than the independent E-value. The conditional E-value uses the number of targets that pass the reporting thresholds. The null hypothesis test posed by the conditional E-value is as follows. Suppose that we believe that there is already sufficient evidence (from other domains) to identify the set of reported sequences as homologs of our query; now, how many additional domains would we expect to find with at least this particular domain’s bit score, if the rest of those reported sequences were random nonhomologous sequence (i.e. outside the other domain(s) that were sufficient to identified them as homologs in the first place)?
(13) i-Evalue: The “independent E-value”, the E-value that the sequence/profile comparison would have received if this were the only domain envelope found in it, excluding any others. This is a stringent measure of how reliable this particular domain may be. The independent E-value uses the total number of targets in the target database.
(14) score: The bit score for this domain.
(15) bias: The biased composition (null2) score correction that was applied to the domain bit score.
(16) from (hmm coord): The start of the MEA alignment of this domain with respect to the profile, numbered 1..N for a profile of N consensus positions.
(17) to (hmm coord): The end of the MEA alignment of this domain with respect to the profile, numbered 1..N for a profile of N consensus positions.
(18) from (ali coord): The start of the MEA alignment of this domain with respect to the sequence, numbered 1..L for a sequence of L residues.
(19) to (ali coord): The end of the MEA alignment of this domain with respect to the sequence, numbered 1..L for a sequence of L residues.
(20) from (env coord): The start of the domain envelope on the sequence, numbered 1..L for a sequence of L residues. The envelope defines a subsequence for which their is substantial probability mass supporting a homologous domain, whether or not a single discrete alignment can be identified. The envelope may extend beyond the endpoints of the MEA alignment, and in fact often does, for weakly scoring domains.
(21) to (env coord): The end of the domain envelope on the sequence, numbered 1..L for a sequence of L residues.
(22) acc: The mean posterior probability of aligned residues in the MEA alignment; a measure of how reliable the overall alignment is (from 0 to 1, with 1.00 indicating a completely reliable alignment according to the model).
(23) description of target: The remainder of the line is the target’s description line,
as free text.
As with the target hits table (above), this table is columnated
neatly for human readability, but you should not write parsers that
rely on this columnation; parse based on space-delimited fields instead.