stacks 这个 软件可以计算你看看的:https://catchenlab.life.illinois.edu/stacks/manual/
populations.sumstats.tsv: Summary statistics for each population
The populations program will calculate a standard set of population genetic statistics for population in the set of data it processes. These values are calculated at every variant site in the metapopulation (that means a site may be fixed in one or more populations, but is variant in at least one population, or across populations). Each variant site will be listed in the file on one line, for each population. If there are three populations in the analysis, each variant site will be listed on three lines, once per population.
- If the analysis is de novo, then the chromosome will be listed as "un" which is short for "unknown" and the basepair will arbitrarily ordered.
- If smoothing is enabled, with the --smooth, or more specific, --smooth-popstats option, then the smoothed columns will have values, otherwise they will be blank. The chromosome and basepair fields will also be populated.
- If bootstrapping is enabled, smoothed windows will be resampled to generate a p-value indicating significance for each of the smoothed statistics, otherwise these columns will be blank.
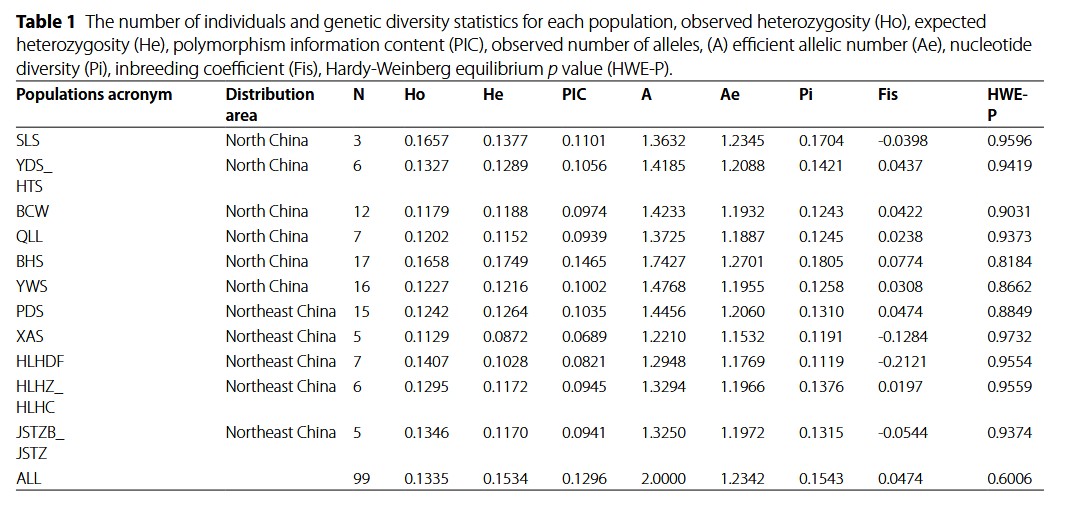
| 1 | Locus ID | Catalog locus identifier. |
| 2 | Chromosome | If aligned to a reference genome. |
| 3 | Basepair | If aligned to a reference genome. This is the basepair for this particular SNP. |
| 4 | Column | The nucleotide site within the catalog locus, reported using a zero-based offset (first nucleotide is enumerated as 0). |
| 5 | Population ID | The ID supplied to the populations program, as written in the population map file. |
| 6 | P Nucleotide | The most frequent allele at this position in this population. |
| 7 | Q Nucleotide | The alternative allele. |
| 8 | Number of Individuals | Number of individuals sampled in this population at this site. |
| 9 | P | Frequency of most frequent allele. |
| 10 | Observed Heterozygosity | The proportion of individuals that are heterozygotes in this population. |
| 11 | Observed Homozygosity | The proportion of individuals that are homozygotes in this population. |
| 12 | Expected Heterozygosity | Heterozygosity expected under Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium. |
| 13 | Expected Homozygosity | Homozygosity expected under Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium. |
| 14 | π | An estimate of nucleotide diversity. |
| 15 | Smoothed π | A weighted average of π depending on the surrounding 3σ of sequence in both directions. A value of -1 indicates that a particular locus was not included in the smoothing operation (likely because it was overlapped by a separate RAD locus that was included). |
| 16 | Smoothed π P-value | If bootstrap resampling is enabled, a p-value ranking the significance of π within this population. |
| 17 | FIS | The inbreeding coefficient of an individual (I) relative to the subpopulation (S). Derived from Hartl & Clark, Principles of Population Genetics, fourth edition, equation 6.4, page 264. |
| 18 | Smoothed FIS | A weighted average of FIS depending on the surrounding 3σ of sequence in both directions. |
| 19 | Smoothed FIS P-value | If bootstrap resampling is enabled, a p-value ranking the significance of FIS within this population. |
| 20 | HWE P-value | The probability that this variant site deviates from Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium. Calculated via an exact test. |
| 21 | Private allele | True (1) or false (0), depending on if this allele is only occurs in this population. |
populations.sumstats_summary.tsv: Summary of summary statistics for each population
The populations program will summarize the standard set of population genetic statistics across the dataset. These values can be replicated by summing the columns in the populations.sumstats.tsv file. For example, the mean value of Π is obtained by summing column 14 in the populations.sumstats.tsv file for one of the populations and dividing by the number of rows.
| 1 | Pop ID | Population ID as defined in the Population Map file. |
| 2 | Private | Number of private alleles in this population. |
| 3 | Number of Individuals | Mean number of individuals per locus in this population. |
| 4 | Variance | |
| 5 | Standard Error | |
| 6 | P | Mean frequency of the most frequent allele at each locus in this population. |
| 7 | Variance | |
| 8 | Standard Error | |
| 9 | Observed Heterozygosity | Mean obsered heterozygosity in this population. |
| 10 | Variance | |
| 11 | Standard Error | |
| 12 | Observed Homozygosity | Mean observed homozygosity in this population. |
| 13 | Variance | |
| 14 | Standard Error | |
| 15 | Expected Heterozygosity | Mean expected heterozygosity in this population. |
| 16 | Variance | |
| 17 | Standard Error | |
| 18 | Expected Homozygosity | Mean expected homozygosity in this population. |
| 19 | Variance | |
| 20 | Standard Error | |
| 21 | Π | Mean value of π in this population. |
| 22 | Π Variance | |
| 23 | Π Standard Error | |
| 24 | FIS | Mean measure of FIS in this population. |
| 25 | FIS Variance | |
| 26 | FIS Standard Error | |
| Notes: There are two tables in this file containing the same headings. The first table, labeled "Variant" calculated these values at only the variable sites in each population. The second table, labeled "All positions" calculted these values at all positions, both variable and fixed, in each population. |
populations.fst_Y-Z.tsv: FST calculations for each pair of populations
If --fstats is specified to the populations program, then FST statistics will be calculated for each pair of populations, as defined in the population map.
- FST will be calculated for each variable site between the pair of populations (different pairs of populations may have different numbers of variable sites).
- A p-value indicating a statistically significant difference in allele frequencies (that is a p-value for the FST measure), is provided by Fisher’s Exact Test in the "FET p-value" column.
- If a reference genome is available and --smooth is specified, these values will be smoothed across chromosomes and those smoothed values will be stored in the "Smoothed AMOVA ST" column below.
- If bootstrapping is enabled, then it will be used to generate p-values for each smoothing window and stored in the "Smoothed AMOVA FST P-value" column.
| 1 | Locus ID | Catalog locus identifier. |
| 2 | Population ID 1 | The ID supplied to the populations program, as written in the population map file. |
| 3 | Population ID 2 | The ID supplied to the populations program, as written in the population map file. |
| 4 | Chromosome | If aligned to a reference genome. |
| 5 | Basepair | If aligned to a reference genome. |
| 6 | Column | The nucleotide site within the catalog locus, reported using a zero-based offset (first nucleotide is enumerated as 0). |
| 7 | Overall π | An estimate of nucleotide diversity across the two populations. |
| 8 | AMOVA FST | Analysis of Molecular Variance FST calculation. Derived from Weir, Genetic Data Analysis II, chapter 5, "F Statistics," pp166-167. |
| 9 | FET p-value | P-value describing if the FST measure is statistically significant according to Fisher’s Exact Test. |
| 10 | Odds Ratio | Fisher’s Exact Test odds ratio. |
| 11 | CI High | Fisher’s Exact Test confidence interval. |
| 12 | CI Low | Fisher’s Exact Test confidence interval. |
| 13 | LOD Score | Logarithm of odds score. |
| 14 | Corrected AMOVA FST | AMOVA FST with either the FET p-value, or a window-size or genome size Bonferroni correction. |
| 15 | Smoothed AMOVA FST | A weighted average of AMOVA FST depending on the surrounding 3σ of sequence in both directions. |
| 16 | Smoothed AMOVA FST P-value | If bootstrap resampling is enabled, a p-value ranking the significance of FST within this pair of populations. |
| 17 | Window SNP Count | Number of SNPs found in the sliding window centered on this nucleotide position. |